Drivetrains:
It is the group of components which delivers engine power to the driving wheels.
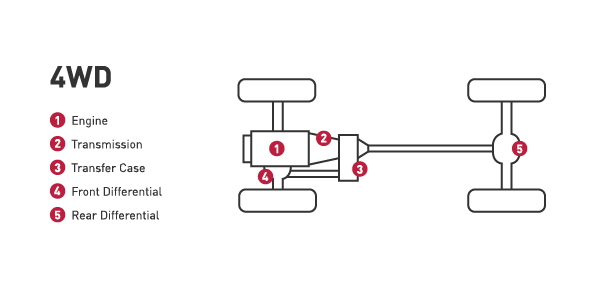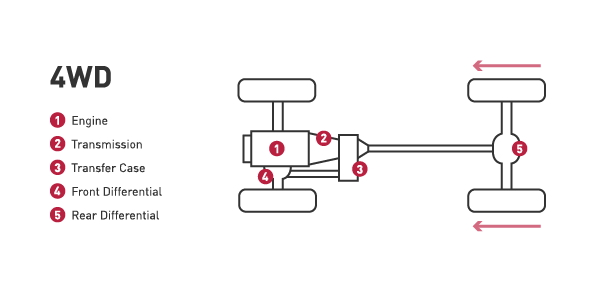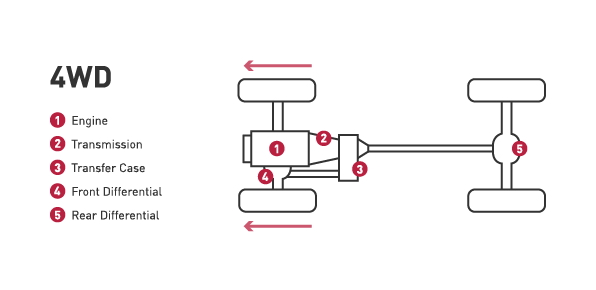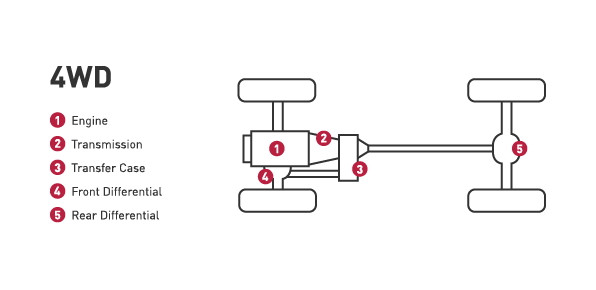
The components of a drivetrain are Engine, Transmission, Drive/Propeller shaft, Differential,Drive axle, Transaxle.
Types of Drivetrains:
There are four types of drivetrains
- Rear-wheel Drive
- Front-wheel Drive
- All-wheel Drive
- Four-wheel Drive
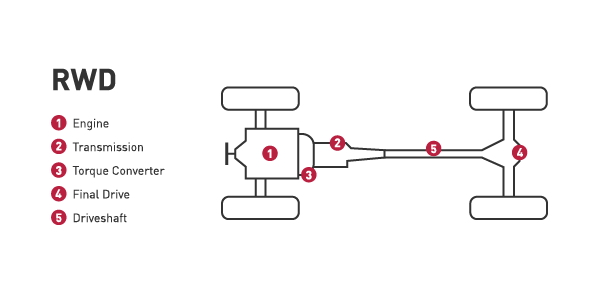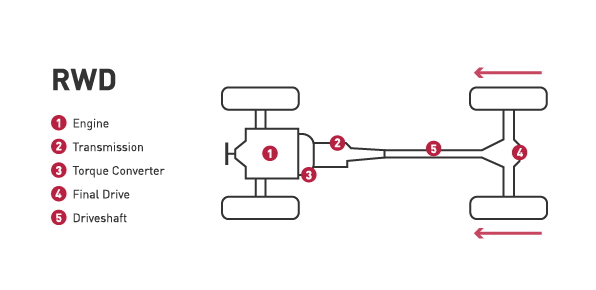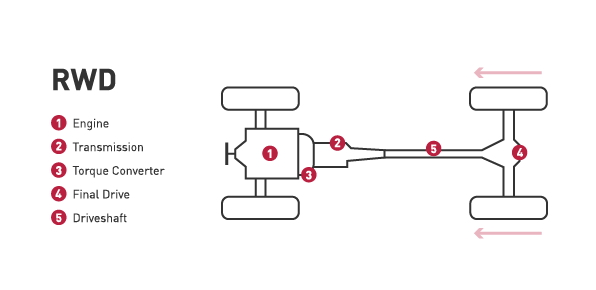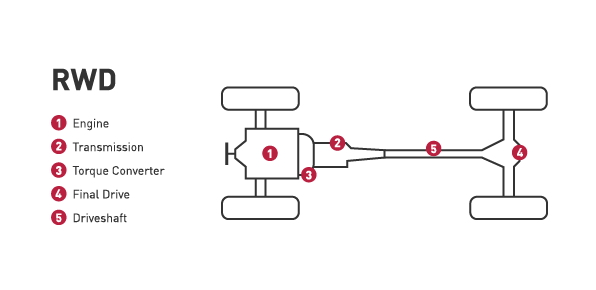
Rear-wheel drive:
- A rear-wheel drive system relies on the rear wheels to deliver the power.
- RWD is commonly found on trucks and performance vehicles, it gives needed traction with heavy loads and optimal handling on performance cars.
- Drawback of rear-wheel drive is reduced traction on slippery roads; this might not be ideal for snowy climate.
Advantages:
- Superior handling.
- Exceptional braking.
- Quick initial acceleration.
- Excellent for performance driving.
- Superior handling.
- Exceptional braking.
- Quick initial acceleration.
- Excellent for performance driving.
Disadvantages:
Front-wheel drive:
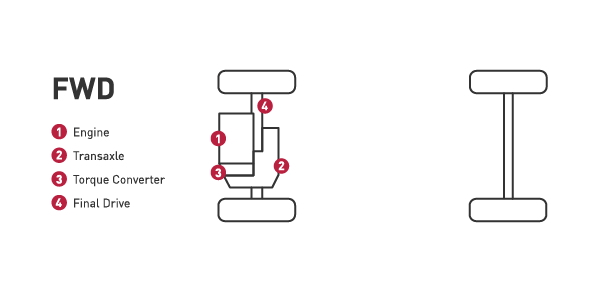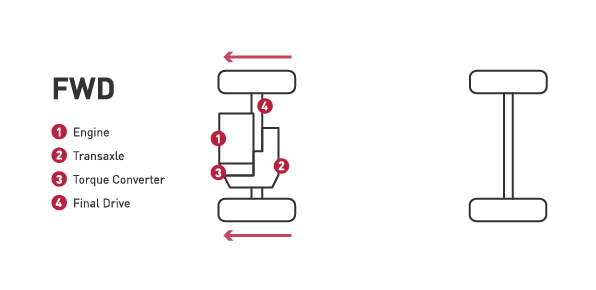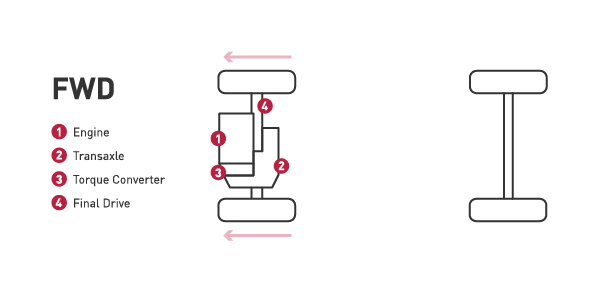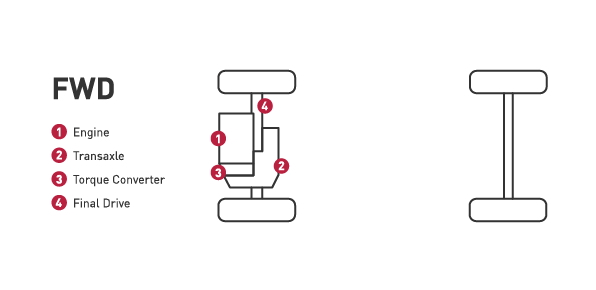
- The majority of vehicles on the road today are using front-wheel drive system. In this system, the front wheels provide the power.
- All of the drivetrain components are located in the front of the vehicle which increases traction in the front wheels.
- Vehicles with front-wheel drive are typically lighter, helping to improve gas mileage.
Advantages:
- Fewer parts mean lower purchase price and repair bills.
- Lighter weight helps vehicle achieve better gas mileage.
- Better traction than rear-wheel drive.
- With most of weight over front wheels, it’s balanced for traction.
- Less aggressive handling is good for new and cautious drivers.
Disadvantages:
- Not as effective in low-traction situations like gravel and ice
- Nose heavy makes it harder to handle in high speeds or with heavy loads.
- Can cause understeer where front wheels lose traction and car drifts outside of the turn.
Four-wheel drive:
- A four-wheel drive system have two drive shafts and a transfer case to deliver power to all four wheels. Today’s 4WD systems are either full-time or part-time.
- In a full-time system, the vehicle automatically switches between two-wheel and four-wheel drive while a part-time system requires the driver to manually engage the four-wheel drive system.
Advantages:
- Excellent for towing trailers or big loads.
- Ideal for serious off-roading, crawling over rocks and moving through mud.
- Powers through deep snow.
- Delivers the traction needed for climbing hills.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than FWD and RWD due to extra parts.
- Lower gas mileage due to heavier drivetrain system.
- Have to remember to engage it in a part-time system.
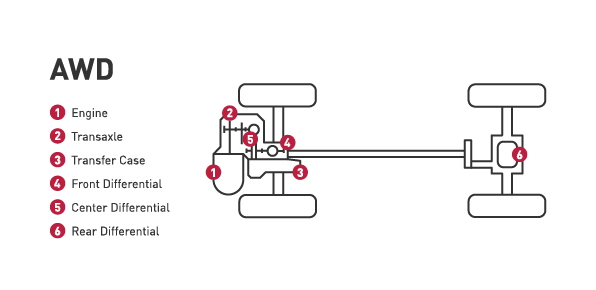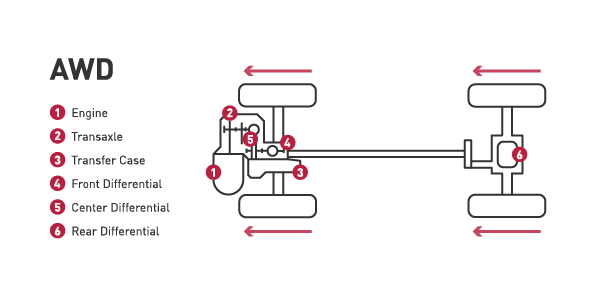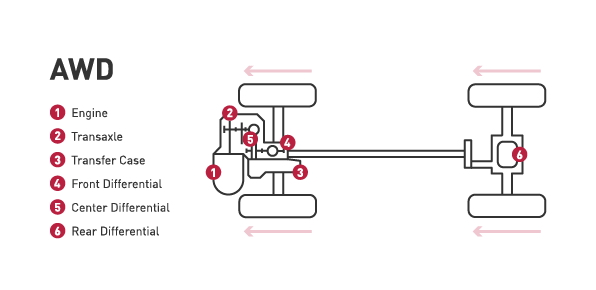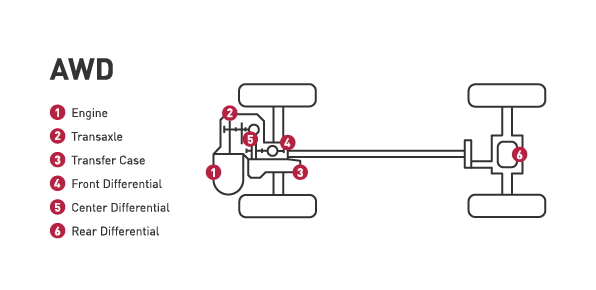
All-wheel drive:
- AWD delivers power to all four wheels. Most all-wheel drive systems are always on, using sensors to determine which wheel needs power.
- However, be aware that systems vary and some all-wheel drive setups stay in two-wheel drive most of the time and only go into all-wheel drive mode when the sensors detect the vehicle is losing traction.
Advantages:
- Better acceleration.
- Improved traction in snow and on wet roads.
- Always on – don’t have to think about engaging the system.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive with more parts than FWD and RWD.
- Worse gas mileage due to vehicle being heavier.
- Can cost more to repair than a FWD or RWD vehicle.


No comments:
Post a Comment